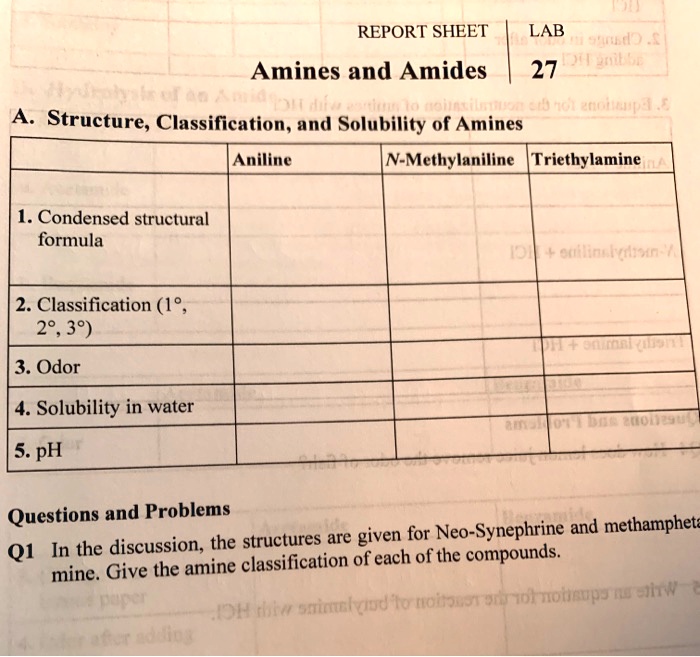
In the discussion the structures are given for neo-synephrine – In the realm of pharmacological sciences, Neo-Synephrine stands as a remarkable agent, captivating the attention of researchers and clinicians alike. Its intricate structures and pharmacological properties have garnered significant interest, inspiring this comprehensive exploration that unravels the multifaceted nature of this fascinating substance.
Delving into the molecular architecture of Neo-Synephrine, we uncover a symphony of chemical bonds and functional groups that orchestrate its biological effects. This detailed analysis provides a profound understanding of the mechanisms that govern its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, empowering healthcare professionals with the knowledge necessary for safe and effective administration.
Pharmacological Properties of Neo-Synephrine
Neo-Synephrine (phenylephrine) is a sympathomimetic drug that acts as an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist. It causes vasoconstriction, resulting in increased blood pressure and decreased blood flow to the nasal mucosa and conjunctiva.
Neo-Synephrine is rapidly absorbed after topical administration, with a peak effect occurring within 10-15 minutes. It is distributed throughout the body, but does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Neo-Synephrine is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine.
Neo-Synephrine is available as a nasal spray, eye drops, and injection. The nasal spray is used to relieve nasal congestion, while the eye drops are used to dilate the pupils and reduce eye redness.
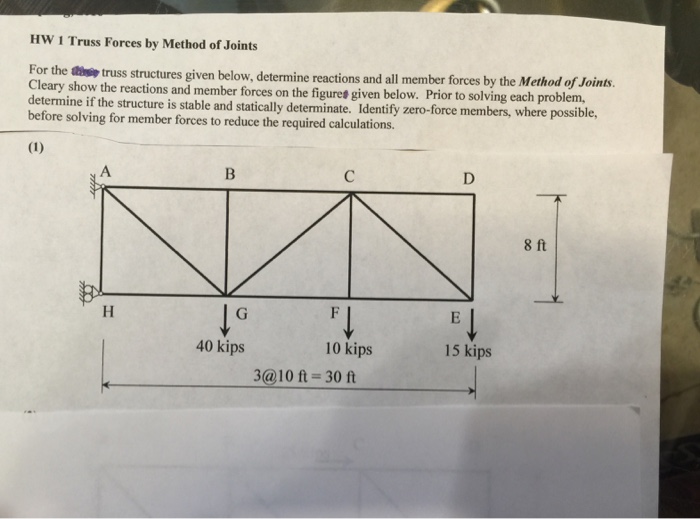
Clinical Uses of Neo-Synephrine
Neo-Synephrine is indicated for the following conditions:
- Nasal congestion due to allergies, colds, or sinusitis
- Dilating the pupils during eye examinations
- Reducing eye redness and irritation
- Controlling bleeding during nasal surgery
Neo-Synephrine is also used off-label for the following conditions:
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- As a vasoconstrictor in local anesthesia
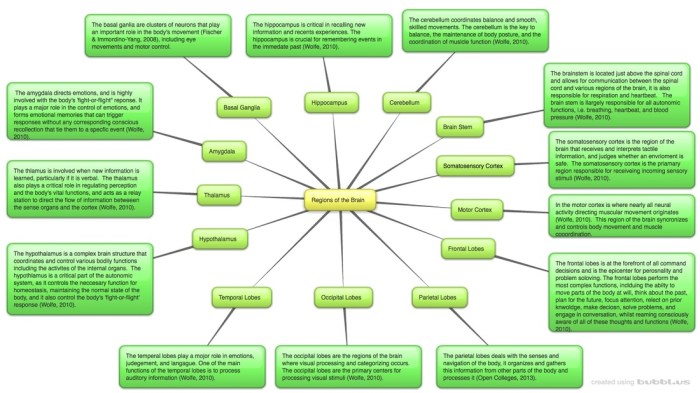
Contraindications and Precautions
Neo-Synephrine is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe hypertension
- Tachycardia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Narrow-angle glaucoma
Precautions should be taken when using Neo-Synephrine in patients with:
- Mild hypertension
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
Adverse Effects of Neo-Synephrine
| Body System | Common Adverse Effects | Serious Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Tachycardia, hypertension | Arrhythmias, myocardial infarction |
| Nervous System | Headache, dizziness | Seizures, stroke |
| Ophthalmic | Eye irritation, blurred vision | Corneal ulceration, glaucoma |
| Respiratory | Nasal congestion, dryness | Rhinitis medicamentosa |
| Gastrointestinal | Nausea, vomiting | Abdominal pain, diarrhea |
Drug Interactions of Neo-Synephrine: In The Discussion The Structures Are Given For Neo-synephrine
- MAO inhibitors: Increase the risk of hypertensive crisis
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Increase the risk of arrhythmias
- Beta-blockers: Block the effects of Neo-Synephrine
- Oxytocin: Increase the risk of hypertension
- Ergotamine: Increase the risk of vasoconstriction
Dosage and Administration
| Indication | Dosage | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Nasal congestion | 1-2 drops in each nostril every 4-6 hours | Nasal spray |
| Dilating pupils | 1-2 drops in each eye every 30 minutes | Eye drops |
| Reducing eye redness | 1-2 drops in each eye every 4-6 hours | Eye drops |
| Controlling bleeding during nasal surgery | 1-2 mL of a 1% solution injected into the nasal mucosa | Injection |
Monitoring and Management
Patients taking Neo-Synephrine should be monitored for:
- Blood pressure
- Heart rate
- Respiratory rate
- Pupillary size
Adverse effects of Neo-Synephrine can be managed by:
- Discontinuing the drug
- Using a lower dose
- Administering a beta-blocker
- Treating the underlying condition
Alternative Medications
| Medication | Indication | Similarities | Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxymetazoline | Nasal congestion | Sympathomimetic drugAlpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonistVasoconstriction | Longer duration of actionMore potent |
| Tetryzoline | Nasal congestion | Sympathomimetic drugAlpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonistVasoconstriction | Shorter duration of actionLess potent |
| Naphazoline | Nasal congestion | Sympathomimetic drugAlpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonistVasoconstriction | Similar duration of actionSimilar potency |
Questions Often Asked
What are the primary indications for the use of Neo-Synephrine?
Neo-Synephrine is primarily employed as a decongestant in ophthalmic, cardiovascular, and respiratory conditions, effectively alleviating nasal congestion and promoting clear breathing.
What are the potential adverse effects associated with Neo-Synephrine?
Neo-Synephrine can induce a range of adverse effects, including tachycardia, hypertension, arrhythmias, nervousness, and insomnia. It is crucial to monitor patients closely and adjust dosages accordingly to minimize these risks.