Determine whether each label describes skeletal or cardiac muscle – In the realm of human biology, the study of skeletal and cardiac muscle holds immense significance. These two distinct muscle types play pivotal roles in movement, circulation, and overall bodily function. Embarking on this discourse, we delve into the defining characteristics, functions, and structural differences between skeletal and cardiac muscle, shedding light on their crucial contributions to human physiology.
Skeletal muscle, responsible for voluntary movement, exhibits a unique cellular structure and arrangement, contrasting sharply with the specialized features of cardiac muscle, which tirelessly pumps blood throughout the body. Understanding these distinctions is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of the human muscular system.
Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle: Structure, Function, and Comparison
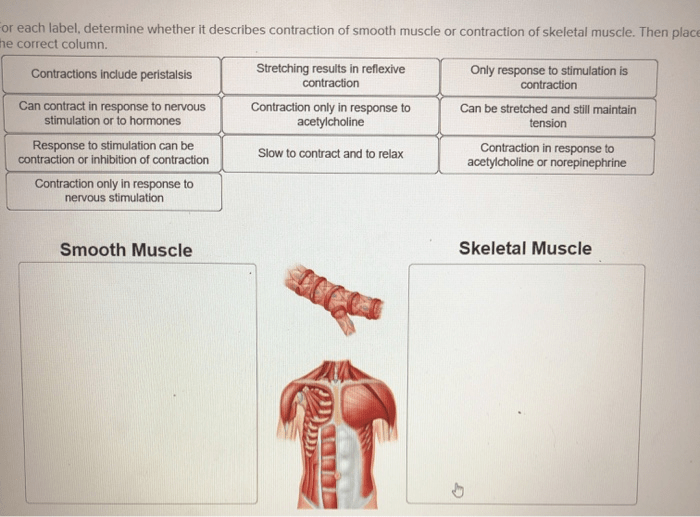
Skeletal and cardiac muscle are two distinct types of muscle tissue with specialized functions in the body. Understanding their key characteristics and differences is essential for comprehending the complex mechanisms of movement and circulation.
Key Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle is responsible for voluntary movement and is attached to bones. Its key characteristics include:
- Multinucleated cells with peripherally located nuclei
- Striated appearance due to alternating bands of actin and myosin
- Organized into bundles called muscle fibers
- Controlled by the somatic nervous system
Key Characteristics of Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle forms the walls of the heart and is responsible for pumping blood. Its key characteristics include:
- Single-nucleated cells
- Striated appearance with intercalated discs
- Branched cells interconnected by gap junctions
- Autorhythmic, meaning it can contract spontaneously
- Controlled by the autonomic nervous system
Examples of Skeletal Muscles and Their Functions
Biceps
Flexion of the elbow
Quadriceps
Extension of the knee
Gastrocnemius
Plantar flexion of the foot
Deltoids
Abduction of the arm
Examples of Cardiac Muscles and Their Functions
Atria
Receive blood from the body and ventricles
Ventricles
Pump blood to the body and lungs
Comparison of Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle Structure, Determine whether each label describes skeletal or cardiac muscle
| Feature | Skeletal Muscle | Cardiac Muscle ||—|—|—|| Cell Shape | Multinucleated, elongated | Single-nucleated, branched || Number of Nuclei | Multiple | One || Arrangement of Myofibrils | Parallel | Interconnected by intercalated discs || Presence of Intercalated Discs | No | Yes |
Functional Significance of Structural Differences
The structural differences between skeletal and cardiac muscle reflect their distinct functions. Skeletal muscle’s multinucleated cells and parallel myofibrils allow for rapid and powerful contractions necessary for voluntary movement. Cardiac muscle’s single-nucleated cells and intercalated discs facilitate synchronized contractions required for pumping blood efficiently.
Function of Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal muscle contracts to produce movement by shortening its sarcomeres. Cardiac muscle contracts to pump blood by squeezing the heart chambers, propelling blood forward. Skeletal muscle contractions are faster and more powerful than cardiac muscle contractions, which are slower and more sustained.
Types of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
Skeletal muscle fibers are classified into three types based on their speed and fatigue resistance:
Type I (Slow-Twitch)
Slow, fatigue-resistant fibers suitable for endurance activities
Type IIa (Fast-Twitch Oxidative-Glycolytic)
Fast, fatigue-intermediate fibers used in activities like sprinting and cycling
Type IIx (Fast-Twitch Glycolytic)
Very fast, fatigue-prone fibers ideal for high-intensity activities like weightlifting
Innervation of Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal muscle is innervated by the somatic nervous system, which allows for conscious control of movement. Cardiac muscle is innervated by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates heart rate and contractility without conscious effort.
FAQ Corner: Determine Whether Each Label Describes Skeletal Or Cardiac Muscle
What is the key difference between skeletal and cardiac muscle?
Skeletal muscle is voluntary, while cardiac muscle is involuntary.
How many nuclei do skeletal muscle cells have?
Multiple nuclei
What is the function of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
Intercalated discs facilitate electrical signal transmission and mechanical coupling between cardiac muscle cells.