One cell organism crossword clue – Embarking on an intellectual journey, we delve into the captivating world of one-cell organisms, a microscopic realm where simplicity belies profound complexity. From their fundamental characteristics to their ecological significance, this comprehensive guide unveils the secrets of these enigmatic life forms, illuminating their role in the intricate tapestry of life.
One-cell organisms, also known as unicellular organisms, represent the most fundamental and ancient form of life on Earth. Their diminutive size, ranging from a few micrometers to several hundred micrometers, belies their remarkable diversity and ubiquity. These organisms inhabit a vast array of environments, from the depths of the oceans to the heights of the atmosphere, showcasing their extraordinary adaptability.
One-Cell Organisms: One Cell Organism Crossword Clue
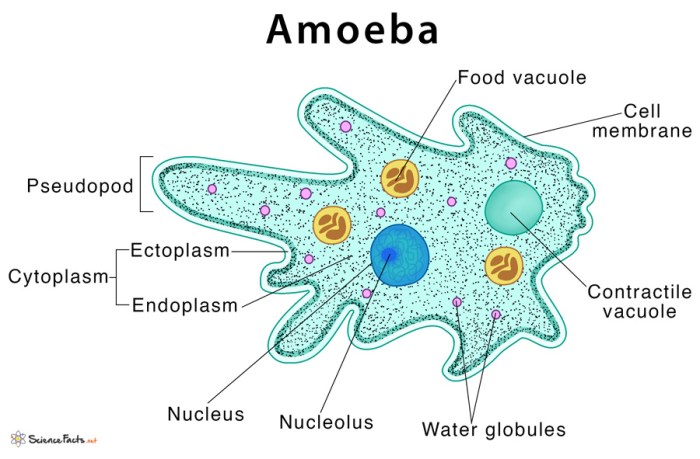
One-cell organisms, also known as unicellular organisms, are the simplest and most abundant form of life on Earth. They consist of a single cell that carries out all the functions necessary for life, including metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
One-cell organisms exhibit a wide range of diversity in terms of their structure, function, and habitat. They can be found in all environments, from extreme environments such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents to more temperate environments such as freshwater lakes and oceans.
Types of One-Cell Organisms, One cell organism crossword clue
One-cell organisms can be categorized into two main groups based on their structure and function: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
- Prokaryotic organismsare the simplest type of one-cell organisms. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Examples of prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archaea.
- Eukaryotic organismsare more complex than prokaryotic organisms. They have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic organisms include protists, fungi, and animals.
Metabolism and Reproduction in One-Cell Organisms
One-cell organisms obtain energy and nutrients through a variety of metabolic processes. Some one-cell organisms are autotrophic, meaning they can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Others are heterotrophic, meaning they must consume other organisms to obtain energy and nutrients.
One-cell organisms reproduce through a variety of methods, including binary fission, budding, and spore formation.
Ecological Significance of One-Cell Organisms
One-cell organisms play a vital role in the Earth’s ecosystem. They are responsible for nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiosis.
One-cell organisms can also have a negative impact on human health and the environment. Some one-cell organisms are pathogens that can cause disease in humans and animals. Others can produce toxins that can contaminate food and water.
Applications and Advancements in One-Cell Organism Research
One-cell organisms have a wide range of applications in biotechnology. They are used in genetic engineering, medical research, and environmental remediation.
Recent advancements in the study of one-cell organisms have led to the development of new technologies that can be used to study the evolution, ecology, and physiology of these organisms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key characteristics of one-cell organisms?
One-cell organisms are characterized by their small size, simple cellular structure, and lack of specialized tissues and organs.
How do one-cell organisms obtain energy and nutrients?
One-cell organisms employ various metabolic strategies to obtain energy and nutrients, including photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, and heterotrophy.
What are the different modes of reproduction in one-cell organisms?
One-cell organisms reproduce through asexual means, such as binary fission, budding, and spore formation, as well as sexual means, involving the fusion of gametes.